The Future of Oncology Hospitals: Advancements, Care, and Patient Outcomes
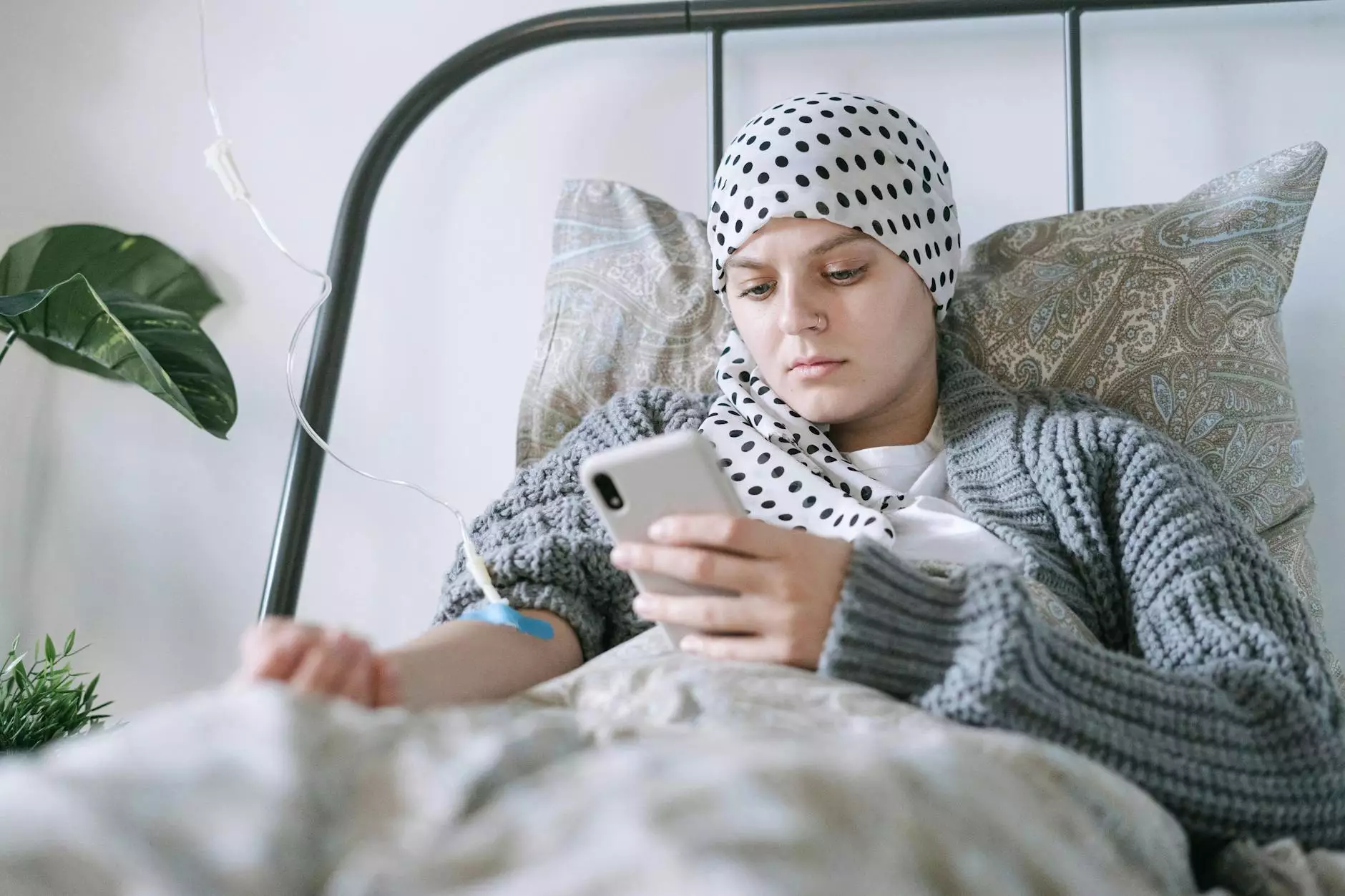

Oncology hospitals play a critical role in the landscape of cancer care, facilitating both the prevention and treatment of various forms of cancer. As the incidence of cancer continues to rise globally, these medical facilities are constantly evolving to meet the growing demands of their patients. This article delves into the multifaceted evolution of oncology hospitals, examining advancements in technology, patient care, treatment methodologies, and the holistic integration of services aimed at improving patient outcomes.
The Importance of Specialized Oncology Care
The fight against cancer is complex and requires a specialized approach. Oncology hospitals are dedicated entities that focus specifically on cancer treatment, bringing together a multidisciplinary team of experts including medical oncologists, surgical oncologists, radiation oncologists, pathologists, nurses, and support staff. This collective expertise is essential to provide comprehensive care:
- Coordination of Care: Patients often undergo multiple types of treatment, including surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. Having a specialized team ensures that all treatments are well-coordinated.
- Access to Clinical Trials: Oncology hospitals often participate in cutting-edge research, giving patients access to the latest therapeutic innovations and experimental treatments.
- Support Services: Comprehensive care plans are not just about medical treatment; they also include psychological support, nutritional counseling, and palliative care, making the experience more holistic.
Advancements in Technology Within Oncology Hospitals
Advancements in technology are transforming the way cancer is diagnosed and treated within oncology hospitals. These innovations have significant implications for early detection, personalized treatment plans, and improved patient outcomes.
1. Precision Medicine
Precision medicine tailors treatment to individual patients based on genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. By analyzing the genetic mutations found within a patient’s tumor, oncologists can select targeted therapies that are more likely to be effective. This approach not only enhances the likelihood of treatment success but also minimizes unnecessary side effects associated with traditional therapies.
2. Advanced Imaging Techniques
Advanced imaging techniques, such as PET scans, MRI, and CT scans, are vital for accurate cancer staging and monitoring progress. Oncology hospitals are increasingly employing these technologies to provide real-time insights into tumor growth and response to treatment, enabling timely adjustments to patient care strategies.
3. Robotic Surgery
Robotic-assisted surgical systems allow surgeons to perform complex procedures with greater precision and smaller incisions. As a result, patients experience less pain, reduced risk of infection, and quicker recoveries. Many oncology hospitals are adopting these systems to enhance surgical outcomes.
4. Telemedicine
Telemedicine has surged during the recent global health crises, providing patients with access to oncology specialists without the need for in-person visits. This technology is especially beneficial for follow-up care and consultation, improving accessibility for patients who live in rural areas or who have mobility issues.
Patient-Centered Care Models
All oncology hospitals understand that the patient experience is crucial for recovery. Implementing a patient-centered care model not only improves satisfaction but also leads to better health outcomes. Below we discuss essential elements of these models:
1. Comprehensive Treatment Plans
A well-rounded treatment plan addresses not just the cancer itself but also the patient's emotional and physical well-being. Oncology hospitals strive to create individualized plans that take into consideration the patient's preferences and lifestyle.
2. Multidisciplinary Tumor Boards
Multidisciplinary teams comprised of specialists from various fields convene for tumor boards to discuss complex cases. This collaborative approach ensures that every aspect of the patient’s care is reviewed and optimized.
3. Psychological Support Services
Psychosocial support is essential for cancer patients. Many oncology hospitals provide access to counselors, support groups, and wellness programs that focus on mental health, coping strategies, and survivorship.
4. Patient Education
Empowering patients through education about their diagnosis, treatment options, and potential side effects is a priority. Oncology hospitals often offer workshops, provide printed materials, and facilitate consultations that equip patients with knowledge about their condition.
The Role of Nutrition in Cancer Care
Nutrition plays a pivotal role throughout the cancer journey, from prevention to recovery. Many oncology hospitals now incorporate dietitians and nutritionists into their care teams, ensuring patients receive personalized dietary advice that supports their treatment protocols.
- Prevention: Healthy nutrition is linked to lower cancer risk. Oncology hospitals promote healthy eating habits to empower patients in managing their health.
- During Treatment: Nutritional support can alleviate treatment-related side effects, boost immune function, and improve overall quality of life.
- Post-Treatment: A well-balanced diet is key to recovery and maintaining long-term health, making nutritional counseling crucial.
Innovative Treatment Options
As research progresses, the treatment landscape for oncology continues to shift dramatically. Here are several innovative approaches currently being used or explored in oncology hospitals:
1. Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy harnesses the body’s immune system to fight cancer. This novel approach has revolutionized treatment for several types of cancer, proving particularly effective in melanoma and some lung cancers.
2. Gene Therapy
Gene therapy attempts to correct genetic abnormalities that lead to cancer. Early clinical trials show promising results, making it a hot topic in oncology research.
3. CAR-T Cell Therapy
Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy modifies a patient’s T cells to target and kill cancer cells more effectively. It has shown immense promise, especially in treating certain blood cancers.
Challenges Facing Oncology Hospitals
Despite the progress, oncology hospitals face numerous challenges that can impede the delivery of optimal care:
- Increasing Patient Volume: The demand for oncology care continues to grow due to an aging population and rising cancer rates, putting strain on resources.
- Rising Costs: Innovative treatments often come with high costs, leading to accessibility issues for certain patient populations.
- Workforce Shortages: The shortage of qualified oncologists and nursing staff presents a significant barrier to providing comprehensive cancer care.
The Future of Oncology Hospitals
The future of oncology hospitals is bright, characterized by continued technological advancements and a shift toward patient-centered care. Here are some key trends shaping the future:
- Integration of AI: Artificial intelligence will play an instrumental role in diagnostics, treatment planning, and patient management, enhancing precision and efficiency.
- Personalized Medicine: As the understanding of cancer genetics deepens, personalized treatment options will continue to burgeon.
- Enhanced Support Systems: The focus will remain on developing comprehensive support systems to address the psychological and emotional needs of patients.
Conclusion
Oncology hospitals are at the forefront of cancer care, evolving continuously to meet the needs of the patients they serve. With advancements in technology, innovative treatment options, and a commitment to patient-centered care, these facilities are not only improving the quality of care but also enhancing the quality of life for those battling cancer. As we look to the future, it is imperative that oncology hospitals remain adaptable and proactive in their approach, ensuring they are equipped to handle the complexities of cancer treatment effectively.